|
 |
|
 |
How to write a business plan
A business plan is... It explains to its audience (often a bank for a loan) how and why the business will be successful (in particular, how well it can satisfy its customers) So also read these sections: (because a business plan should be presented clearly, concisely and enthusiastically).
What a business plan should look like
(each typed section must be on a new page):
1. Title page Title of the plan with the date and names of the business and its author.
2. Contents A list of the sections listed with page numbers, starting with the introduction and ending with a list of any appendices.
3. Introduction Introduction to the business and purpose of the plan.
4. Executive summary A clear and concise (one page maximum) summary of the plan’s key conclusions and recommendations.
5. Main section of the plan Eight sub-sections discussing the reasons for the business’s success (the 8 C’s – see below and business success).
6. Acknowledgements Thanks to anyone who has helped with the plan.
7. Bibliography Alphabetical listing of any books, websites and other references used.
8. Appendices Detailed reference material (e.g. statistics and spreadsheets). Put the key points of this material in the plan and then refer the reader to these appendices.
Main section of the business plan (the 8 C’s)
1. Culture and purpose
a) culture The business’s key values and how they are put into practice (e.g. customer satisfaction, respect for the individual and the pursuit of excellence).
b) vision statement A future business ideal. For example, the aim of Walt Disney (pictured right) was “to bring happiness to millions”.
c) mission statement A clear and concise (preferably one sentence) statement of your business purpose.
2. Customers
a) your market research - showing:
b) customer profile (describing a typical customer in terms of needs, income, social class, etc).
c) your unique selling proposition (USP) Unique and superior benefits and solutions you can offer your customers.
d) your 7’s (strategy, structure, systems, staff, skills, style of management and shared values, or corporate culture) How effectively they are geared towards delighting your customers.
e) your marketing strategy
Find more detail in these sections:
3. Competitors
a) who your competitors are Don’t define your market so narrowly that you ignore key competitors (e.g. film and TV are in the entertainment business).
b) beating competitors How you will avoid their strengths and exploit their weaknesses.
c) the level of competition Can competitors easily imitate your product or do your innovation and product distinctiveness give you the edge?
d) your competitive advantage What can you give customers your competitors can’t? – see competitive advantage.
4. Change, learning and innovation Are you continually prepared to innovate, change (quickly adapting to changes in customer requirements), improve and learn from your successes and failures?
5. Competencies
a) your distinctive capabilities (or core competencies) These make you better than your competitors e.g. innovation and customer service.
b) your skills in key activities Marketing, innovation, operations (or production), finance and leadership/management.
6. Commitment The motivation and passion of the owner(s) and employees.
7. Cash and profit
a) cash Have you enough cash to pay your bills? - include a cash flow forecast (see cash flow management)
b) budgets These show planned sales and costs for the next 12 months (see budgeting and cost control).
c) profit performance Are your sales revenue (turnover), profits and profit margins rising in the next five years? See analysing accounts.
d) your break-even point How much you need to sell before you make a profit. See costing and break-even analysis.
8. Corporate strategy
a) the objectives of your strategy Your business can beat competitors either on price (through lower costs) or superior quality/image (called product differentiation).
b) communication of objectives How strategic objectives are clearly communicated to employees.
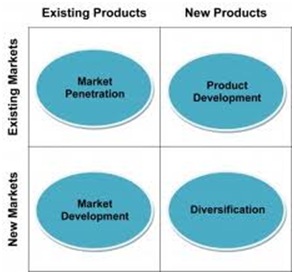
c) Ansoff’s matrix Use Ansoff's matrix (see below and corporate strategy) to show how future sales can be increased by changing products and/or the markets in which they are sold (e.g. overseas customers).
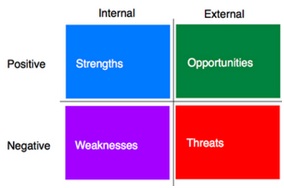
d) a SWOT analysis Use a SWOT analysis (see below and corporate strategy) to identify the business’s:
Show how you will:
e) resources Show you have the resources to successfully implement your strategy Resources are usually summarized as the 4 M’s:
Have you the best suppliers in terms of quality, price and delivery?
Key quotes explained “You plan a tower that will pierce the clouds. Lay first the foundation of humility” - St. Augustine (a Christian philosopher, pictured right). Successful implementation of a business plan requires the humility to accept your ignorance and other people’s skills and advice so that your customers are totally satisfied.
“Our goals can only be reached through the vehicle of a plan, in which we must fervently believe and upon which we must vigorously act. There is no other route to success”, - Pablo Picasso (Spanish artist, pictured right). Be passionate and proactive but prepare yourself, too. “Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe” said the American president, Abraham Lincoln.
“No battle plan survives contact with the enemy”, - Colin Powell (former American general and Secretary of State, pictured right). Defeating the enemy (competitors) requires changing the plan to cope with new circumstances (particularly new customer requirements).
Best books
Richard Branson, Losing My Virginity (1998) How Branson (pictured right) turned Virgin into a global success through a business plan based upon customer satisfaction, constant innovation, employee commitment, cost control and Branson’s charismatic leadership.
Judi Bevan, The Rise and Fall of Marks and Spencer...and How It Rose Again (2007) - pictured right The story of the successes and failures of the British retailer, Marks and Spencer, which shows the importance of continually changing your business plan to satisfy new customer requirements. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
||
| Copyright © wisdomtowin.com All Rights Reserved | ||
|