|
 |
|
 |
|
|
||
Michael Porter (1947- )
American Harvard Business School professor and leading expert on strategy and the competitive advantage of companies and countries (pictured right).
Key books
Competitive Strategy (1980)
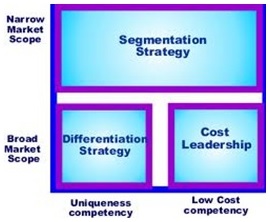
Successful companies achieve “competitive advantage” (better value than competitors) by concentrating on one of three “generic strategies”:
1. Cost leadership Selling to a mass market with lower costs and prices than competitors.
2. Differentiation Selling to a mass market at a high price with a product perceived by customers as unique and superior to competitors.
3. Focus Selling to a particular customer category (a market segment or niche e.g.rich or poor). This segmentation strategy will concentrate on:
An organization will fail, when it is “stuck in the middle” - having a strategy that isn't focused on one of the generic strategies outlined above. Such a company will only make profits if its:
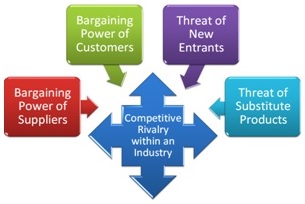
Causes of a highly profitable industry structure
1. High entry barriers Deterring new competitors because of your:
2. Low competitive rivalry (because of a high industry growth rate, minimizing competition for market share).
3. Low buyer power (due to a superior product, or a monopoly).
4. Low supplier power (the company is big relative to the supplier like supermarkets).
5. Little or no threat of substitutes (due to good value relative to price).
These five factors are now referred to as Porter’s five forces model.
Competitive analysis is also important which analyses competitors' strengths and weaknesses (so that strengths can be avoided and weaknesses exploited). A company must respond to competitors' market signals indicating their strategic intentions.
Porter summarized the book’s message in a 1996 Harvard Business Review article, What Is Strategy? - “Competitive strategy is about being different”, he said.
Key quote on industry analysis All five competitive forces jointly determine the intensity of industry competition and profitability.
Key quote on strategy Competitive strategy involves positioning a business to maximize the value of the capabilities that distinguish it from its competitors.
Competitive Advantage (1985) (see for more detail Competitive Advantage in the Business Books section)
Successful companies have “sustainable competitive advantage” (perpetually better value than competitors). This requires:
The value chain has five primary activities: 1. Inbound logistics The receipt, storage and distribution of supplies (or inputs) required for operations.
2. Operations Converting inputs into the final product.
3. Outbound logistics The collection, storage and distribution of products to buyers.
4. Marketing and sales Persuading people to buy the products and making it easier for them to do so.
5. Service After-sales support.
These primary activities are supported by four support activities:
1. Human resource management Hiring and motivating employees.
2. Procurement Buying.
3. Technology development Research and development.
4. Firm infrastructure Support managerial functions like finance and planning.
Within each primary and secondary activity, there are three further activities:
Key quotes on competitive advantage Competition is at the core of the success or failure of firms. Competitive advantage grows fundamentally out of value a firm is able to create for its buyers that exceeds the firm’s cost of creating it.
Key quote on business success The first fundamental determinant of a firm’s profitability is industry attractiveness.
The Competitive Advantage of Nations (1990) (see for more detail The Competitive Advantage of Nations in the Business Books section)
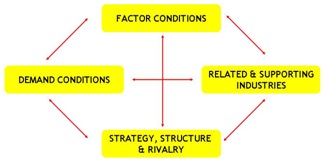
A diamond model is used to describe four interrelated factors which (in addition to chance and government action) will decide whether or not a country achieves international success in a particular industry: 1. Factor conditions Relating to factors of production, for example:
2. Demand conditions The popularity of the industry’s product with customers.
3. Related and supporting industries The international competitiveness of suppliers and associated industries.
4. Firm strategy, structure and rivalry The competitiveness of domestic companies that will spur them to improve and compete globally.
Key quotes on economic growth Productivity is the prime determinant in the long run of a nation’s standard of living. Incentives, effort, perseverance, innovation and especially competition are the source of economic progress in any nation and the basis for productive, satisfied citizens.
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Copyright © wisdomtowin.com 2025 All Rights Reserved | ||
|