|
 |
|
 |
Michael Porter, Competitive Advantage (1985)
American Harvard Business School professor and leading expert on strategy and the competitive advantage of companies and countries (pictured right). His reputation is based on this book and two others:
See also... Michael Porter in the Management Gurus section.
Book summary
What increases profits?
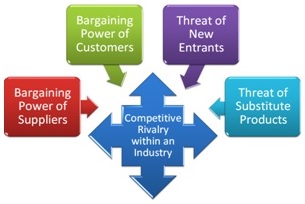
1. Industry attractiveness The profitability and competitiveness of the company’s industry. These are determined by the five industry forces, discussed by Porter in his previous book,
Competitive Strategy (1980):
For more detail see Industry analysis in the Management Topics section
2. Sustainable competitive advantage Continually providing better value to customers than competitors through:
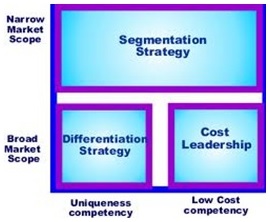
Generic strategies
1. Cost leadership Being the lowest cost (and price) producer in the industry.
2. Differentiation Providing customers with something better and different - for example:
3. Focus (or segmentation)
Why is being “stuck in the middle” bad? This means having a strategy that isn't focused on one of the generic strategies outlined above. An organization will usually fail, if this happens, because the high costs of differentiation mean that... A firm can normally only achieve either cost leadership or differentiation. But there are three situations where they can be achieved simultaneously:
a) poor performance of competitors (because they are stuck in the middle).
b) a firm’s cost advantage resulting from:
c) a major innovation (that only the firm possesses).
The value chain
Successful companies maximize value to customers at each stage of the company’s “value chain”:
1. Inbound logistics The receipt, storage and distribution of supplies (or inputs) required for operations.
2. Operations Converting inputs into the final product.
3. Outbound logistics The collection, storage and distribution of products to buyers. 4. Marketing and sales Persuading people to buy the products and making it easier for them to do so.
5. Service After-sales support.
These five primary activities are supported by four support activities: 1. Human resource management (hiring and motivating employees).
2. Procurement (buying). 3. Technology development (research and development).
4. Firm infrastructure (support managerial functions like finance and planning). Within each primary and support activity, there are three further activities:
a) direct (directly creating customer value).
b) indirect (helping to create customer value)
c) quality assurance (getting quality right).
Key quotes on competitive advantage Competitive advantage grows fundamentally out of value a firm is able to create for its buyers that exceeds the firm’s cost of creating it. Industry leadership is not a cause but an effect of competitive advantage
Key quote on business success Competition is at the core of the success or failure of firms.
Key quote on customers Superior value stems from offering lower prices than competitors for equivalent benefits or providing unique benefits that more than offset a higher price. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
||
| Copyright © wisdomtowin.com All Rights Reserved | ||
|