|
 |
|
 |
|
|
||
Competitive advantage
Competitive advantage is... Creating better value for customers than competitors (so increasing sales and profits).
How to gain competitive advantage
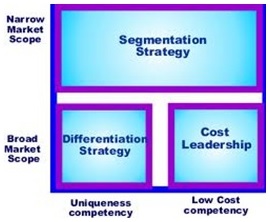
1. Michael Porter’s generic strategies These are three strategies to beat competitors, discussed in Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter’s (pictured right) book, Competitive Strategy (1980):
a) differentiation Selling to a broad market something unique and better than competitors.
b) cost leadership Selling to a broad market with lower costs (and so lower prices) than competitors.
c) focus (or segmentation) Selling to a particular customer group (a market segment or niche) - see market segmentation Focus can be achieved by selling something:
Porter recommends pursuing only one of these strategies, or a business will become “stuck in the middle”, achieve none of them and lose its competitive advantage. But the best organizations contradict this conclusion by achieving both differentiation and cost leadership.
2. Michael Porter’s value chain The value chain shows the activities an organization must carry out to delight its customers. Michael Porter (pictured right) in his book, Competitive Advantage (1985) divided these activities into primary and support:
Primary activities
a) Inbound logistics The delivery and storage of goods and services required by the organization.
b) Operations Producing or selling the organization’s product(s).
c) Outbound logistics Distribution of product(s) to customers.
d) Marketing and sales Persuading people to buy the product(s).
e) Service After-sales service.
Support activities
a) Human resource management Employee recruitment, training and motivation.
b) Procurement Purchasing of goods and services.
c)Technology development Using technology to improve products (e.g. research and development), raw materials and processes (e.g. production).
d) Infrastructure The organization’s structure and systems (e.g. finance).
All these activities (and their co-ordination to achieve customer satisfaction) must be done better than competitors.
3. Core competencies These are skills and technologies that enable an organization to satisfy its customers better than its competitors (e.g. Apple’s superiority in design and innovation) See core competencies for more detail.
4. Change and innovation An organization can never be complacent. It must be continuously learning, improving and innovating to beat its competitors. It will have to satisfy and create new customers with brilliant new products. Speed of action and adaptability to change are vital.
Key quotes explained
“If you don’t have competitive advantage, don’t compete”, Jack Welch, ex-boss of General Electric (pictured right) . Competitive advantage is a prerequisite of successful business, resulting, says Welch, from an organization’s ability to translate “learning into action rapidly”.
“No leadership position is more than a temporary position”, Peter Drucker in his book, Managing for Results (pictured right) If you are complacent, competitors will overtake you. So constant innovation is vital.
“A clever fighter is one who not only wins but excels in winning with ease”, Sun Tzu, general in ancient China (pictured right) Seek the quickest and easiest route to competitive advantage. “Speed is the essence of war”, Sun Tzu also said.
Best books and articles
Michael Porter, Competitive Advantage (1985) Competitive advantage is created by generic strategies (from Porter’s 1980 book, Competitive Strategy) and the value chain (see above). For more detail see Competitive Advantage in the Business Books section.
PIMS (Profit Impact of Market Strategy), 1987 A research study of 450 American companies which found that quality is the most important source of competitive advantage.
Gary Hamel (pictured right) and C.K. Prahalad (pictured below), Competing for the Future (1994) Competitive advantage comes from:
For more detail see Competing for the Future in the Business Books section.
Kenneth Andrews (pictured right), The Concept of Corporate Strategy (1971) Competitive advantage depends on an organization’s “distinctive competence” i.e. “what it can do particularly well”.
George Stalk (pictured right) and Thomas Hout (pictured right below), Competing Against Time (1990)
The most powerful source of competitive advantage is speed (in new product development, production, sales and marketing)
Pankaj Ghemawat (pictured right below), Sustainable Advantage (1986 Harvard Business Review article)
Competitive advantage comes from:
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Copyright © wisdomtowin.com 2025 All Rights Reserved | ||
|